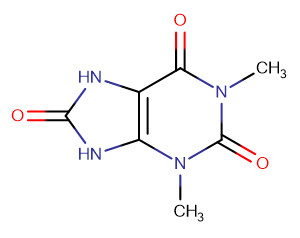
13-Dimethyluric acid
CAS No. 944-73-0
13-Dimethyluric acid( —— )
Catalog No. M21423 CAS No. 944-73-0
13-Dimethyluric acid is a product of theophylline metabolism in man. It is one of the purine components in urinary calculi.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name13-Dimethyluric acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description13-Dimethyluric acid is a product of theophylline metabolism in man. It is one of the purine components in urinary calculi.
-
Description13-Dimethyluric acid is a product of theophylline metabolism in man. It is one of the purine components in urinary calculi.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorHuman Endogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number944-73-0
-
Formula Weight196.16
-
Molecular FormulaC7H8N4O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 5 mg/mL (25.49 mM)
-
SMILESCN(C(N1)=C(C(N2C)=O)NC1=O)C2=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Alloepipregnanolone
Alloepipregnanolone is a pregnane with anesthetic hypnotic and sedative properties.
-
Norgestimate metabol...
Norelgestromin is one of the active metabolites of norgestimate.It is a steroidal progestin used in contraceptive patches, where it is combined with the estrogen ethinyl estradiol.
-
Dodecanedioic acid
Dodecanedioic acid is a dicarboxylic acid used in the synthesis of the engineering plastic nylon 612.Dodecanedioic acid is used as a base oil in industrial production.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


